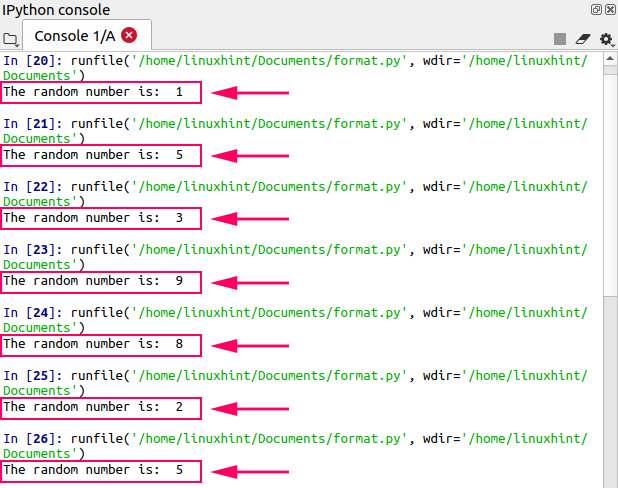
As the name suggests the random module is used to play with random data in Python. This method is generally used to create random numbers, shuffle list items and pick a random item from sequential data objects. The Python built-in random module is used to generate random numbers (e.g. integers or floats) within a specific range. It also allows generating strings and lists with random elements. The Numpy library also provides the random module to generate random data structures. In this tutorial, you learned how to use Python to randomly select items from a Python list.
You learned how to use the random module and its choice(), choices(), and sample() functions to select an item or items with and without replacement. You also learned how to apply weights to your sampling to give more preference to some items over others. Finally, you learned how to use the seed() function to be able to reproduce our results. I'd like to create random list of integers for testing purposes. I know generating random numbers is a time-consuming task, but there must be a better way.
You'll have learned how to use these functions to modify the selection of random elements from a Python list. When we talk about generating random numbers in Python, the random module comes to mind. This module has different functions to generate random numbers based on your requirement. The randint() function returns a random integer between the start and end numbers provided within the function. Use the numpy.random.randint() function to generate random integers. The result is a Python list containing the random numbers.
To generate a list of random integers we can use the randint() method. It has the same name as the method we have seen in the Python built-in random module but it's more flexible. To get random elements from sequence objects such as lists, tuples, strings in Python, use choice(), sample(), choices() of the random module.
Shuffling data and initializing coefficients with random values use pseudorandom number generators. These little programs are often a function that you can call that will return a random number. The random module holds the function random.choices(). It is useful to select multiple elements from a list or a single element from a given sequence. Giving names, verbs, and nouns in the form of a list. It will take the random string from every declared variable.
Finally, it combines all the elements and generates a random sentence. Here we are using the randrange function to get the random sentence. Both random.choice() and random.choices() functions can be used in selecting multiple random items, but both of them can pick repetitive elements.
If we want to pick multiple items without repetition we have to use the random.sample() function. A random refers to the collection of data or information that can be available in any order. The random module in python is used to generate random strings. The random string is consisting of numbers, characters and punctuation series that can contain any pattern.
The random module contains two methods random.choice() and secrets.choice(), to generate a secure string. Let's understand how to generate a random string using the random.choice() and secrets.choice() method in python. In order to choose items randomly with replacement, we can use the random.choices() method. Similar to the random.sample() function, the function accepts a list and a number of elements, k. Since we can choose an item more than once, the value for k can actually exceed the number of items in the list. Being able to work with random elements is an important skill to learn in Python.
It has many wide applications, such as in data science and in game development. For example, if you're building a card game, you may want to choose a card at random. Python comes with a helpful module, random, which we'll explore in this tutorial in helping you work with random item selection. In the random module, there is a set of various functions that are used to create random numbers.
Sometimes, there may be a need to generate random numbers; for example, while performing simulated experiments, in games, and many other applications. This article explains random number generation in Python using the various functions of the random module. It returns a list of items of a given length which it randomly selects from a sequence such as a List, String, Set, or a Tuple.
This function returns random integers from the "discrete uniform" distribution of the integer data type. Random.randrange is one of the popular methods to generate random elements. It can generate random numbers, elements, string, or a sentence. If the start range is not specified, 0 will be the start value. The random module provides a randrange function which return a random integer number between 0 to k-1 . We can use this function to get a random index number and using that index number we can get the item from the list.
With this trick, we will have the item as well as the item's index number. The random module has many methods and choice() is one of those. We can pick a random item from a non-empty sequence object such as list, tuple, and string with the method.
We can use the random.choice() function if we want to select a random item from a list, tuple, or string. This function accepts a sequential object like list, string, and tuple as an argument and returns a random item or element from them. To create an array of random integers in Python with numpy, we use the random.randint() function.
The random module is a built-in module to generate the pseudo-random variables. It can be used perform some action randomly such as to get a random number, selecting a random elements from a list, shuffle elements randomly, etc. In the above example, we return a random integer between 1 and 10.
We can also generate a list of random numbers between 1 and 10 using the list comprehension method. List comprehension is a concise, elegant way to generate lists in a line of code. Choice() returns one random element, and sample() and choices() return a list of multiple random elements.
Sample() is used for random sampling without replacement, and choices() is used for random sampling with replacement. An array of random integers can be generated using the randint() NumPy function. This behavior is provided in the sample() function that selects a random sample from a list without replacement. The function takes both the list and the size of the subset to select as arguments. Note that items are not actually removed from the original list, only selected into a copy of the list. The choice() function implements this behavior for you.
For integers, there is uniform selection from a range. Random.choice() is also another method to select random elements. This will return the random elements from the set, tuple, or list. For selecting multiple random values from a tuple we can use the random module choices function. The choice function returns a random element from a sequence like a list, tuple etc.
There, you have a list of given numbers or codes that are part of the draw. The choice function can be used to pick a number randomly. In this section, you'll learn how to use Python to select multiple random elements from a list without replacement. Sampling without replacement refers to only being able to pick a certain element a single time.
The module comes with a number of helpful functions that allow us to randomly select or sample from a Python list. We can use numpy.random.choice() to pick any number from list of 1 to 10 numbers. It uses the numpy.arange() function to generate the required range and selects a number from that sequence and stores it in the array.
Random.choices() returns multiple random elements from the list with replacement. This is a very Pythonic and readable way to create a list of random integers. You can stop reading right away and use it in your own code. Yes, you can generate random integers, see the above examples.
This tutorial explains several ways to generate random numbers list in Python. Here, we'll mainly use three Python random number generation functions. These are random.randint(), random.randrange(), and random.sample(). With the choice() function we can only select one item from the list or any other sequential object.
If we want to select multiple random items from a list, we have to run the choice function inside a loop. In the above examples, we have already used the choice function to pick a random item from a list. Let's see another example of selecting a random element value from a list. And this is all that is required to create an array of random integers in Python with numpy. Into this random.randint() function, we specify the range of numbers that we want that the random integers can be selected from and how many integers we want.
You can use the sample() function of the random module of Python. It returns a k-length list of unique elements chosen from the population. The random.randrange() method returns a randomly selected element from the range created by the start, stop and step arguments. Using Python random package we can generate random integer number, generate random number from sequence, generate random number from sample etc. We've accessed the list in random indices using randint() and randrange(), but also got random elements using choice() and sample(). Random.sample() returns multiple random elements from the list without replacement.
Similar to integers and floating-point sequences, a generic sequence can be a collection of items, like a List / Tuple. The random module provides useful functions which can introduce a state of randomness to sequences. Similar to generating integers, there are functions that generate random floating point sequences.
The random module is a built-in function useful to get the random elements from the given sequence. Declaring some set of names, verbs, and nouns to get a random sentence. Using while condition to display the random sentence. Using secret.choice() to get the random elements from the list. A secret module is a built-in function that is useful to generate random elements. Using random.choice() to get the random elements from the list.
In this program, we are using random.randint() to generate a random sentence. Write a python script that randomly chooses the same item from the list every time the random.choice method is called. Suppose we have two lists old_users and new_users, and we want to select a random name from these two lists. In such cases, we first need to add both the list making it a single list, and select a random item using the choice function. If we want to select a random item from a set object we first need to convert that object into a tuple or list, using the tuple() and list() functions.
In the code below, we select 5 random integers from the range of 1 to 100. In this article, we show how to create an array of random integers in Python with Numpy. As we can see in the above output, the random.sample() method returns a string in which all characters are unique and non-repeating. Whereas, the random.choice() method returns a string that may contain repetitive characters. So, we can say that if we want to generate a unique random string, use random.sample() method. The uniform function of the random module also returns the floating point random number.
The difference is, you may specify a range, unlike the random function that returns a random number between (0.0 – 1.0). Now you know how to generate random numbers, random strings, and random lists in Python. In the next section, you'll learn how to pick random elements with given weights in a list in Python.
In the next section, you'll learn how to use Python to pick random elements from a list with replacement. The random.choice() method returns a randomly selected element from a non-empty sequence. Hello everyone, in this tutorial, we will learn to generate random numbers except a particular number in a Python list.
We are going to use random.choice() method with the list comprehension technique to get the desired result. Random.choices returns a k-sized list of elements selected at random with replacement. But subjectively, I'd use the first or second method based on list comprehension to create a list of random floats or integers. The example below demonstrates generating an array of random integers. This function takes three arguments, the lower end of the range, the upper end of the range, and the number of integer values to generate or the size of the array. Random integers will be drawn from a uniform distribution including the lower value and excluding the upper value, e.g. in the interval .